Study Guide
Field 128: Deaf or Hard of Hearing
Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
Note: In this test, T S D H H indicates "teacher of students who are deaf or hard of hearing."
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
Subarea 1—Understanding Students Who Are Deaf or Hard of Hearing
Objective 001—Apply knowledge of the auditory system and identify factors affecting the development of students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
1. A T S D H H reviews the results of a recent language assessment for a kindergarten student. The teacher uses this information to design appropriate instruction to address the student's receptive and expressive language in their preferred communication mode. Which of the following considerations is most important when interpreting this data to plan effective language instruction?
- causation (genetic or acquired)
- age of onset (prelingual or postlingual)
- type (conductive, sensorineural, or mixed)
- degree (mild, moderate, severe, or profound)
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 002—Apply knowledge of the historical, legal, and ethical foundations of education for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
2. Which of the following features of American Sign Language (A S L)/English Bilingual programs distinguish them from other programs for students who are deaf or hard of hearing?
- A S L/English Bilingual programs emphasize use of residual speech and hearing among students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- A S L/English Bilingual programs advocate for A S L as the primary language of students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- A S L/English Bilingual programs focus on mainstreaming and inclusion in general education settings.
- A S L/English Bilingual programs combine both auditory and visual communication for instruction.
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Subarea 2—Assessing Students, Developing Individualized Programs, and Building Collaborative Partnerships
Objective 003—Apply knowledge of various assessment instruments and assessment practices for evaluating the strengths and needs of students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
3. A T S D H H is conducting a functional listening evaluation of a seventh-grade student who is hard of hearing. Which of the following types of information is gained by conducting this evaluation?
- student's visual access
- language comprehension
- student's auditory access
- content-level vocabulary knowledge
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 004—Apply knowledge of procedures for conducting assessments and for interpreting and communicating the results of assessments to address the individual strengths and needs of students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
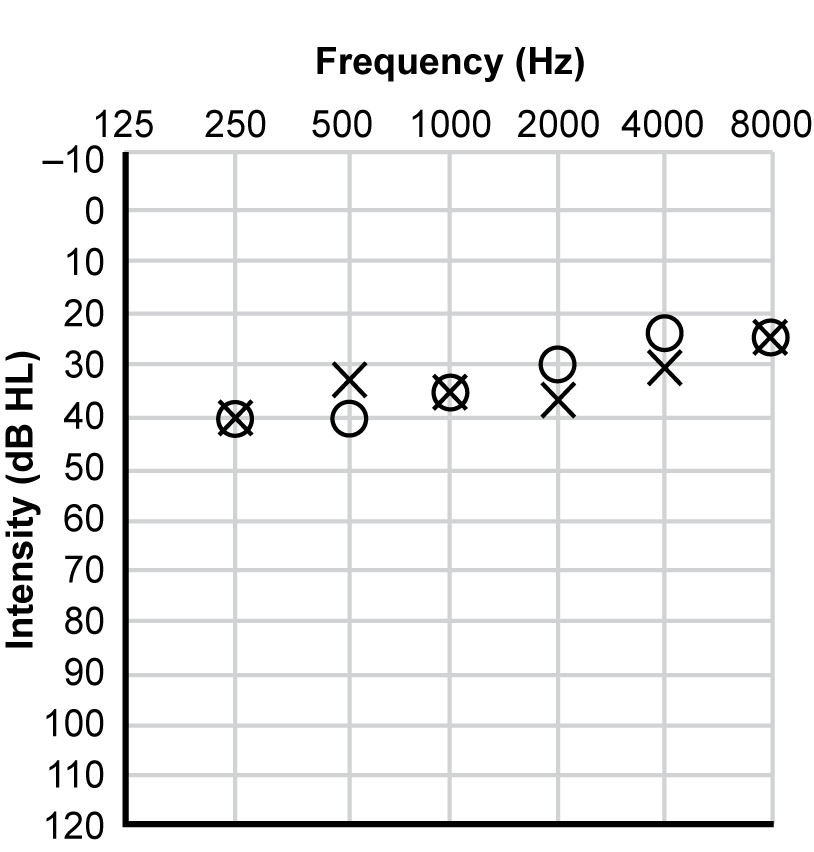
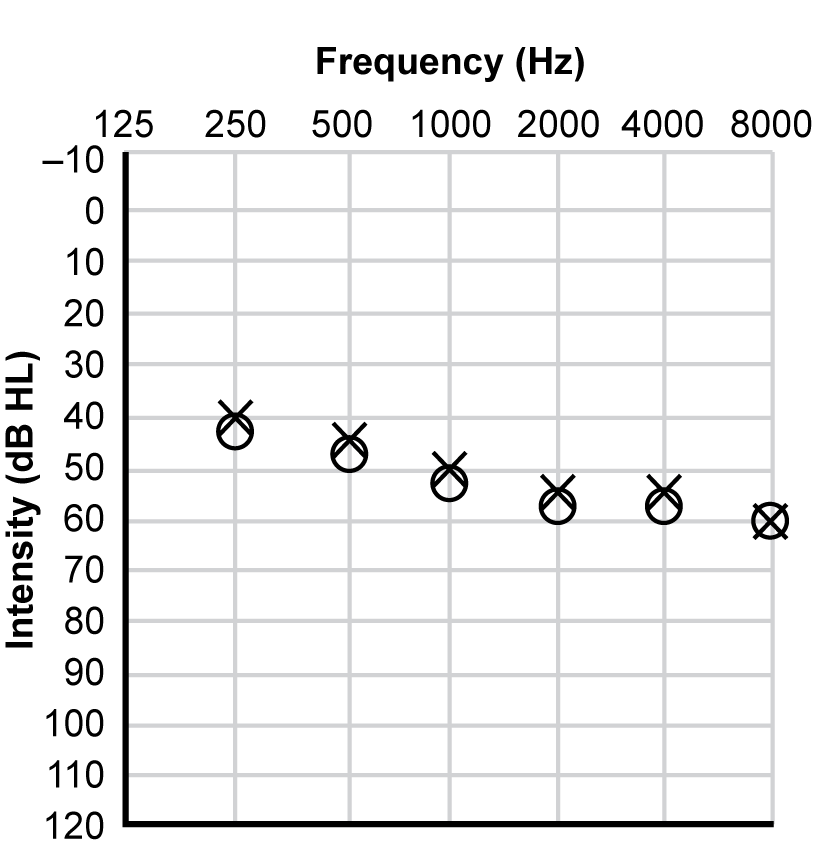
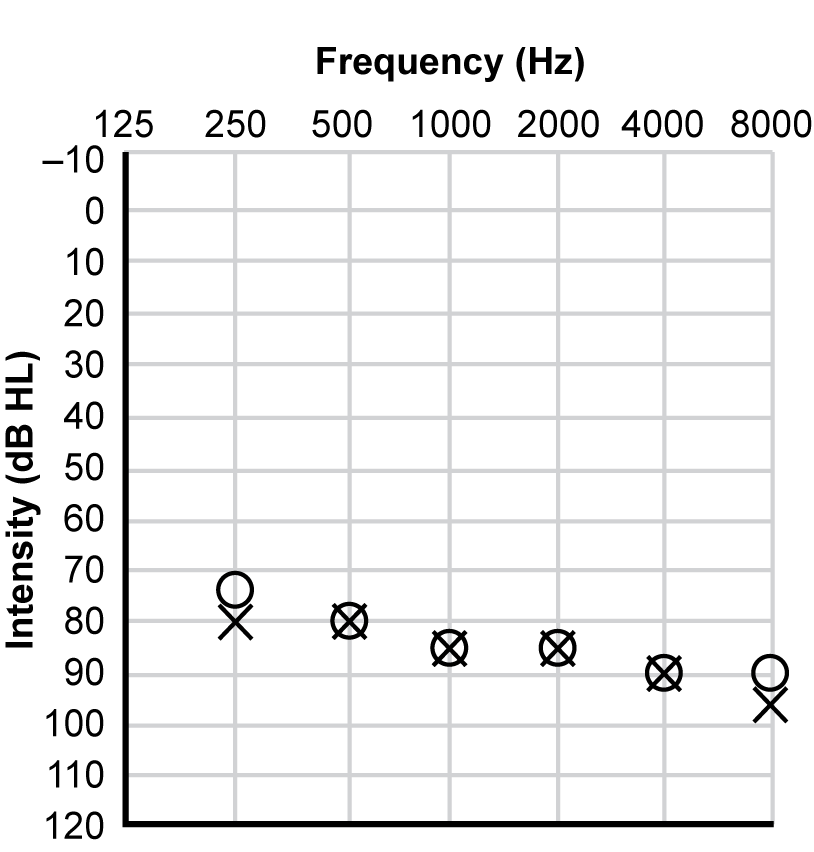
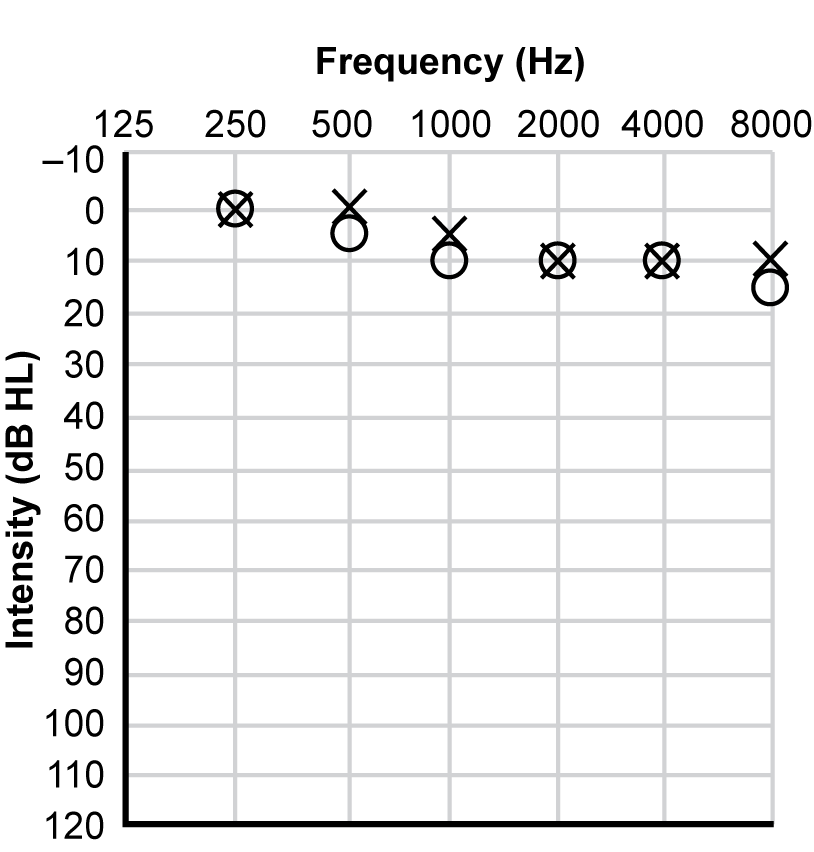
4. Which of the following audiograms best illustrates the hearing status of a student who has slight difficulty understanding conversation, particularly involving the speech sounds S, H, and F?
Responses are presented as results of pure-tone-hearing tests referred to as an audiogram. Each audiogram is labeled "Intensity (dB HL)" on the vertical axis and "Frequency (Hz)" on the horizontal axis. On the vertical axis, the first ordered set of numbers is minus 10, representing minus 10 decibels in the upper left-hand corner of the graph. The value of the set of numbers, representing decibels, increase by ten at each point until reaching 130 in the lower left hand corner of the graph. On the horizontal axis, the numbers 125, 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000, and 8000 represent the frequencies measured in hertz on the top of the graph. "O" indicates the right ear, whereas "X" indicates the left ear.
For response A, the data on the graph shows that 250 hertz was heard at 40 decibels in both the right and left ears, 500 hertz was heard at 40 decibels in the right ear and 35 decibels in the left ear, 1000 hertz was heard at 35 decibels in both the right and left ears, 2000 hertz was heard at 30 decibels in the right ear and 35 decibels in the left ear, 4000 hertz was heard at 25 decibels in the right ear and 25 decibels in the left ear, and 8000 hertz was heard at 25 decibels in both the right and left ears.
For response B, the data on the graph shows that 250 hertz was heard at 42 decibels in the right ear and 40 decibels in the left ear , 500 hertz was heard at 48 decibels in the right ear and 45 decibels in the left ear, 1000 hertz was heard at 52 decibels in the right ear and 50 decibels in the left ear, 2000 hertz was heard at 58 decibels in the right ear and 55 decibels in the left ear, 4000 hertz was heard at 58 decibels in the right ear and 55 decibels in the left ear, and 8000 hertz was heard at 60 decibels in both the right and left ears.
For response C, the data on the graph shows that 250 hertz was heard at 75 decibels in the right ear and 80 decibels in the left ear, 500 hertz was heard at 80 decibels in both the right and left ears, 1000 hertz was heard at 85 decibels in both the right and left ears, 2000 hertz was heard at 85 decibels in both the right and left ears, 4000 hertz was heard at 90 decibels in both the right and left ears, and 8000 hertz was heard at 90 decibels in the right ear and 95 decibels in the left ear.
For response D, the data on the graph shows that 250 hertz was heard at zero decibels in both the right and left ears, 500 hertz was heard at 5 decibels in the right ear and zero decibels in the left ear, 1000 hertz was heard at 10 decibels in the right ear and five decibels in the left ear, 2000 hertz was heard at 10 decibels in both the right and left ears, 4000 hertz was heard at 10 decibels in both the right and left ears, and 8000 hertz was heard at 15 decibels in the right ear and 10 decibels in the left ear.
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A.
Objective 005—Apply knowledge of the procedures for developing, implementing, and amending Individualized Education Programs (I E Pees), Individualized Family Service Plans (I E Pees), and transition plans for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
5. According to the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (I D E A), when developing the special factors component of an Individualized Education Program (I E P) for a student who is deaf or hard of hearing, the I E P team is required to:
- place the student in the general education class setting for at least 50% of the school day.
- provide the student with approved mentors whose primary mode of communication mirrors the student's.
- consider the student's mode of communication and opportunities for direct communication with students and staff.
- ensure that goals related to transition reflect the data and relevant information from the student's transition assessment.
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C.
Objective 006—Apply knowledge of ways to promote and develop collaborative partnerships to support students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
6. Which of the following strategies would most effectively support access to a whole-class read-aloud for a third-grade student who is deaf and who uses an educational interpreter in the classroom?
- seeking out a comparable text for the student to read independently with the interpreter
- providing a copy of the text to the classroom interpreter to read in advance of the read-aloud
- preparing a summary of the text for the interpreter to sign to the student during the read-aloud
- asking the interpreter to work individually with the student and read the text separately from the class
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Subarea 3—Developing and Promoting Language and Communication
Objective 007—Apply knowledge of principles of language acquisition and communication development for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
7. A first-grade T S D H H is helping students improve sign accuracy.
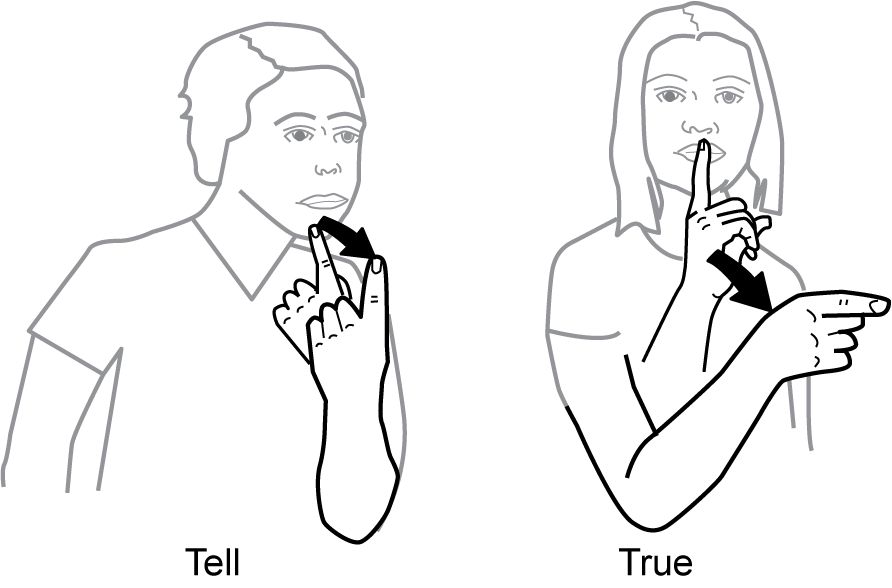
There are two illustrations of people signing.
The individual on the left is bending their left elbow, holding their hand with palm facing their body and extending their index finger upward, holding the rest of their hand with fingers closed. Their index fiber is located at in front of their chin. There is an arrow indicating that they are moving their arm away from their body slightly, with their index finger remaining pointing upward and palm remaining toward their body. The word "tell" is written below this illustration.
The individual on the right is bending their right elbow, extending their index finger and holding the rest of their hand with fingers closed. Their hand is held with their palm facing left and their index finger is held near their lips. There is an arrow indicating that that they are moving their hand away from their body, with the palm remaining oriented to the left. The word "true" is written below this illustration.
Which of the following parameters of American Sign Language (A S L) distinguishes between these two signs?
- location
- movement
- handshape
- palm orientation
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D.
Objective 008—Apply knowledge of ways to facilitate language and communication skills for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
8. A first-grade T S D H H contextualizes the text while reading aloud to the class. The text on one page says:
Jenny was so tired, but she couldn't sleep.
The teacher signs:
Jenny had a long day. She is very tired. When she lays down in the bed to sleep, she cannot stop thinking and has a hard time falling asleep.
Which of the following statements most accurately explains the research-based rationale for the teacher's use of this read-aloud strategy?
- It helps build context and background knowledge for students.
- It provides for greater student engagement.
- It prioritizes grammar and syntax.
- It increases English vocabulary.
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A.
Subarea 4—Promoting Student Learning and Independence
Objective 009—Apply knowledge of methods for creating learning environments and experiences that encourage active engagement and access to instruction for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
9. A T S D H H observes a first-grade classroom to provide feedback on environment accessibility for a student who has cochlear implants. The student currently uses hearing assistive technology (H A T) regularly. Which of the following recommendations would be the most beneficial to reduce background noise in the learning environment?
- The teacher should remove desks and add tables in the room.
- The teacher should place tennis balls on each of the chair legs.
- The teacher should seat the student near the source of the instruction.
- The teacher should place the student's desk in the front of the classroom.
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 010—Apply knowledge of strategies and methods to individualize instruction for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
10. A T S D H H plans activities to support self-advocacy skills related to employment for students in eleventh grade. Which of the following student activities would best promote achievement of this goal?
- developing role-playing scenarios about how to request reasonable accommodations
- sharing a variety of digital personal calendars to practice time-management skills
- modeling how to create a personal budget for calculating expenses
- asking students to complete an interest inventory self-assessment
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A.
Objective 011—Apply knowledge of strategies for promoting the social-emotional competence and independence of students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
11. A seventh-grade student who is deaf completes the following self-assessment prior to the student's yearly Individualized Education Program (I E P) meeting.
|
Self-Assessment Checklist: Directions: Circle the number to indicate the level of comfort you have for each task from 1 (not comfortable) to 5 (very comfortable). |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I can: | |||||
| take care of assistive technology needs (FM, batteries, captioning). | 1 | 2 | 3 | The number 4 is circled. | 5 |
| explain my hearing status and related implications. | 1 | The number 2 is circled. | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| interact with peers during noninstructional periods. | 1 | 2 | 3 | The number 4 is circled. | 5 |
| access video, text, and captioning services with minimal support. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | The number 5 is circled. |
| ask the interpreter for clarification when needed. | The number 1 is circled. | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Based on the student's reporting, the T S D H H should develop additional goals for the student to address:
- self-esteem.
- self-advocacy.
- peer interaction.
- assistive technology.
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B.
Objective 012—Apply knowledge of principles and methods for preparing, selecting, using, and adapting specialized materials, equipment, and assistive technology to provide access for students who are deaf or hard of hearing.
12. A student reports that their hearing aid is not working, even after changing the battery. Prior to referring the issue to the audiologist, which of the following steps should the T S D H H take when troubleshooting this issue?
- removing the connecting tube from the ear hook and listening for feedback
- taking the ear mold off the connecting tube and listening for noise
- moving the volume control switch to ensure the setting is on high
- changing the program settings
- Answer. Enter to expand or collapse. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A.